Freakish African Snails the Size of an Adult Fist
Giant African snail species are on the list of the 100 most harmful invasive alien species in the world, but the Giant African snail is easily adapted to life in regions outside its natural habitat and is considered one of the biggest land snails.
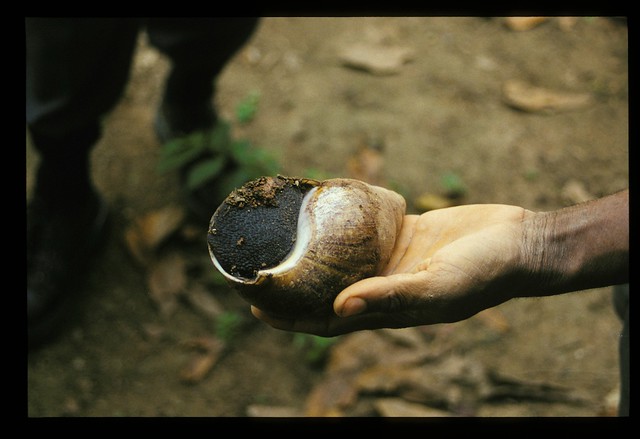

Freakish Giant African snails live on all continents except Antarctica.

The shell is generally reddish-brown in color with weak yellowish vertical markings but coloration varies with environmental conditions and diet. A light coffee color is common. In Africa, from Morocco to Mozambique it lives along the edges of forests but can live on the banks of rivers and streams, shrublands, agricultural areas, plantations, gardens, wetlands and in various urban sites.
Giant African snails are active during the night, and during the day it remains asleep, often buried beneath the ground to stay safe from predators. It is not a social species as it lives all its life alone; Not even after laying eggs, it establishes any bond with its offspring. An important part of the anatomy of this snail is a structure in the mouth similar to a tongue, which is called the radula. It has small teeth that allow snails to scrap the food before eating it.
The Giant African Land Snails are hermaphrodite which means that they have the reproduction organs for both males and females, so they have the capability to self-fertilize, but they do not usually do it. They mate in the traditional way.
Eggs hatch in anything from a few hours to 17 days. Snails mature at around 5 to 15 months, depending on the temperature (with cold winter temperatures inducing hibernation and delaying sexual maturity). The giant African snail lifespan can be up to 9 years, with 5-6 years being the normal range.
Giant African snails are also a general nuisance when found near human habitations and can be hazardous to drivers, causing cars to skid. Their decaying bodies release a bad odor and the calcium carbonate in their shells neutralizes acid soils, altering soil properties and the types of plants that can grow in the soil. The natural predators of this species are caterpillars, ground beetles, other species of snails, and many types of vertebrates.
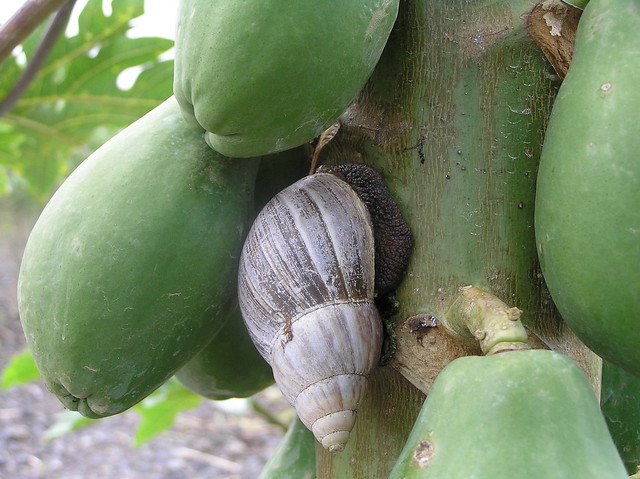 |
| Giant African snail-eating papaya |
Believed to be originally from East Africa, the Giant African land snail is also known as the kalutara snail.
The giant African land snail is the common name used to describe any of the three snail species native to Africa.
The giant African snails are (Achatina fulica), the giant Ghana tiger snail (Achatina achatina), and margies (Archachatina marginata).
Together we build awareness that boost harmony, education, and success, below are more links to articles you will find thought provoking.
- Historical African Country Name
- Top 20 Largest Countries in Africa
- How many countries does Africa have?
- Roots of Africanized Christianity Spiritual Songs
- Chocolate Processing Facts History and Recipes
- Awesome Kenyan Woman
- Land is Not For Women in Sierra Leone
- African Kente Cloth Facts
- Accra the Ghanaian Capital Ultimate Mall Experience

 Since 2007
Since 2007



